What is Exposure?
There are two main types of Exposure Testing: Outdoor exposure testing and accelerated weathering testing using an artificial light source.
- Outdoor Exposure Testing
- The way to see how climates actually affect specimens installed outside. Exposing plastics, rubbers, metals, and coatings used for vehicles and building materials to outdoor daylight causes deformation, discoloration, rust, and other kinds of deterioration.
Those materials must have long-term durability, and it is important to know how materials are affected by exposing them to outdoor environments and the durability of the materials. Exposure testing refers to testing that is performed to determine the durability of materials.
According to JIS Z2381 (General requirements for atmospheric exposure testing), exposure testing is defined as, "A test exposing materials under atmospheric or shielded environments to evaluate their chemical and physical properties and changes."
Pros:This test reproduces results more accurately.
Cons: It requires an extensive amount of time.
- Accelerated Weathering Testing Using an Artificial Light Source
- To reproduce the conditions of the indoors and outdoors such as sunlight, temperature,
humidity, and precipitation artificially, thereby facilitating degradation to predict the lifespan
of products and materials quickly.
Pros:It can be experimented based on short term.
Cons:It is hard to assess deterioration through general usage accurately.
As such, we are striving to build a more accurate method assessment by designing our outdoor exposure testing and accelerated weathering testing to gather more data over a longer time period.

Are You Running into These Type of Issues?
There are different types of deterioration. Through the use of exposure testing, we can assess the conditions and amount of time it takes for a product to deteriorate. As a precaution against product failure and factors contributing to failure, we assist with resolve any issues you have, and engage in the research and development of new products. Feel free to contact us.
Click pictures to see more details
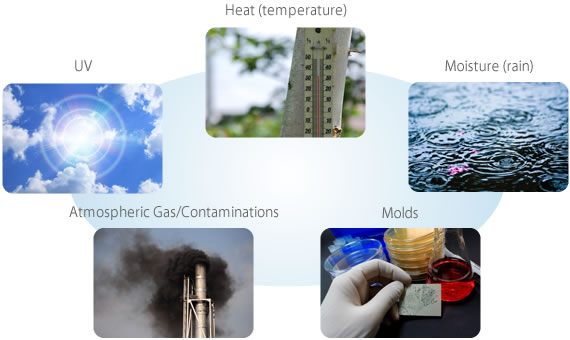
Main Causes of Deterioration
What then, are the causes of deterioration? It is not merely the passage of time that is involved. Deterioration is also influenced by things such as UV, heat, and the natural environment.